蜡样芽胞杆菌群(Bacillus cereus group)为革兰氏阳性菌[1-2],广泛分布于土壤等环境中。其中含有12个同源性很高的种,包括常见的食品污染菌和条件致病菌蜡样芽胞杆菌(Bacilluscereus,Bc)、昆虫病原菌苏云金芽胞杆菌(Bacillus thuringiensis,Bt)、人畜病原菌炭疽芽胞杆菌(Bacillus anthracis,Ba)、具有独特真菌样大而卷发样菌落形态的蕈状芽胞杆菌(Bacillusmycoides,Bm)和假蕈状芽胞杆菌(Bacillus pseudomycoides,Bpm)以及韦氏芽胞杆菌(Bacillus weihenstephanensis,Bw)[3];2010年后又添加了耐高温具有细胞毒性的Bacillus cytotoxicus[4]、用于动物营养的益生菌Bacillus toyonensis[5]、乳品中分离的耐低温具有细胞毒性腐败菌的维德曼芽胞杆菌(Bacillus wiedmannii)[6]、环境中分离的兵马俑芽胞杆菌(Bacillusbingmayongens is)、大山芽胞杆菌(Bacillus gaemokensis)和Bacillus manliponensis6个新种[7-9]。该群内各种在分子水平上基因组同源性极高,其表型和致病性的差别主要由可移动遗传因子—质粒所决定,然而质粒可以丢失、消除和结合转移,导致其种之间分类界定争议较大[10-11]。蜡样芽胞杆菌是我国常见的食源性条件致病菌,苏云金芽胞杆菌在农业上多用于生物农药,炭疽芽胞杆菌是人畜共感染并且具有高致死率,各自具有重要的研究价值,如何有效区分它们有重要研究价值。
蜡样芽胞杆菌群中12个种在常规的16S rRNA序列分析中具有99%~100%相似性,无法进行种间区分[12]。多位点序列分型(multilocus sequence typing,MLST)是一种基于核酸序列测定的细菌分型方法,Bacillus cereus PubMLST数据库选取了glpF、gmk、ilvD、pta、pur、pycA和tpi共7个常见管家基因片段进行测序,该法准确度高、重现性好,便于全球不同实验室的数据比对分析[13]。目前PubMLST数据库中已有50多个国家2 453条菌株的信息,是蜡样芽胞杆菌群信息最丰富、准确的全球数据平台。
Mega是生成系统进化树较常用的软件,可用于分析来自物种或种群的DNA和蛋白质序列数据[14];Phyloviz软件是适合PubMLST数据库配套使用的可结合序列型和菌株基本信息进行多维度聚类分析的软件[15];IQ-tree是2014年基于最大似然(maximum likelihood,ML)法推出的建树软件,具有准确、快速、灵活等特点,特别适用于大数据的系统发育分析[16-17]。ModelFinder是快速、精确的基于模式选择法的系统发育的算法。基于该大数据平台,本研究以Bacillus cereus PubMLST数据库为数据来源,采用常用的分子进化遗传软件Mega,以及更适合大数据分析的Phyloviz和IQ-tree软件分析探讨Bc群内不同种之间的系统进化关系。
1 材料与方法
1.1 软件
进化树软件MEGA 6.06、IQ-tree、Phyloviz 1.1。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 菌株信息的搜集
Bacillus cereus PubMLST数据库[18]中共有来自于全球50多个国家蜡样芽胞杆菌群的2 453条数据,从中筛选出具有完整序列信息的蜡样芽胞杆菌群菌株的信息。目前,Bacillus cereus PubMLST数据库中尚未包含2010年及其之后发表的6个新种信息。
1.2.2 邻接法系统发育树分析
采用MEGA 6.06软件中的邻接(neighbor joining,NJ)法构建系统进化树。
1.2.3 最小生成树分析
采用Phyloviz1.1软件[19-20]对Bacillus cereus PubMLST数据的来源、国别、致病性、序列型(sequence type,ST)[21]进行统计,计算得出各自在全体数据的数量、总体中的比例,并作出相应可视化图片、表格等。运用goeBURST Full最小生成树(minimum spanning tree,MST)[22]中的距离算法作出蜡样芽胞杆菌群的MST,通过数据组信息中的ST编号与菌株详细信息关联,对MST中的编号信息进行关联分析。
1.2.4 ML法系统进化树分析
采用MAFFT v5[23-24]对所有序列进行比对,基于Linux系统运行的IQ-Tree[25]进行核酸模型检测,以ML法构建系统进化树。
2 结果与分析
2.1 蜡样芽胞杆菌群数据分析
从Bacillus cereus PubMLST数据库中共筛选出1 329株有效数据,7个管家基因片段拼接后全长为2 829 bp[26]。包括蜡样芽胞杆菌及其变种共计864株,占总数比为65.01%;苏云金芽胞杆菌及其变种345株,占总数比为25.96%;炭疽芽胞杆菌共61株,占总数比为4.59%;韦氏芽胞杆菌、蕈状芽胞杆菌、假蕈状芽胞杆菌分别为33、21、5株,占总数比分别为2.48%、1.58%、0.37%。其中,全球五大洲数据及未注明地区数据的信息详见表1。除未明确标出地区的326条数据外,亚洲、欧洲和北美洲的蜡样芽胞杆菌菌群的菌株数明显高于南美洲、非洲和大洋洲。
表1 蜡样芽胞杆菌群在全球的分布
Table 1 Global distribution of Bacillus cereus group
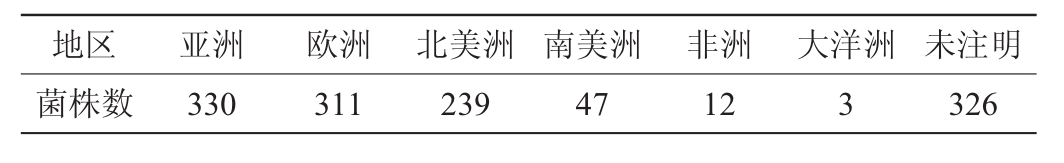
地区 亚洲 欧洲 北美洲 南美洲 非洲 大洋洲 未注明菌株数 330 311 239 47 12 3 326
去除未明确标注分离来源的605株菌株信息,724株菌株的分离来源见图1。由图1可知,来源于土壤、奶制品、其他种类食品的菌株居多,也有来自环境和临床样本如病人的肺部组织、肝脏组织以及血液等的菌株。
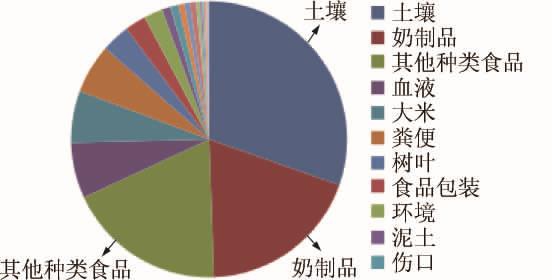
图1 蜡样芽胞杆菌群分离源的分布
Fig.1 Distribution of isolation sources of Bacillus cereus group
2.2 蜡样芽胞杆菌群遗传分析
2.2.1 蜡样芽胞杆菌群最小生成树分析
蜡样芽胞杆菌群的最小生成树见图2。

图2 蜡样芽胞杆菌群的最小生成树
Fig.2 Minimum spanning tree of Bacillus cereus group
由图2可知,蜡样芽胞杆菌及其变种分布最为广泛,散布于整个最小生成树的各个分支上;苏云金芽胞杆菌及其变种多数集中于左下部一支较大的进化分支上,少数菌株却分散在其他所有进化分支上;而炭疽芽胞杆菌最集中,聚集在左下角进化分支的远端,与其同在一分支上的近缘菌株有蜡样芽胞杆菌和苏云金芽胞杆菌;韦氏芽胞杆菌相对集中,并与部分蕈状芽胞杆菌、蜡样芽胞杆菌和少量苏云金芽胞杆菌交织分布在同一进化分支上。
蕈状芽胞杆菌和假蕈状芽胞杆菌原为同一个种,具有大而粗糙发散的卷发样菌落,与蜡样芽胞杆菌群内其他种菌株在菌落、表型上差异显著,后因脂肪酸组成差异而区分为两个不同的种[27]。假蕈状芽胞杆菌数量较少,在进化树中分布相对集中,而蕈状芽胞杆菌零散地分布在进化树中多个分支上,与它们较为接近的菌株却是蜡样芽胞杆菌;耐低温、菌落小而光滑的韦氏芽胞杆菌和部分蕈状芽胞杆菌最为接近。
2.2.2 ML法蜡样芽胞杆菌群的系统进化树分析
7对管家基因经多基因联合后采用ML法构建系统进化树,结果见图3。
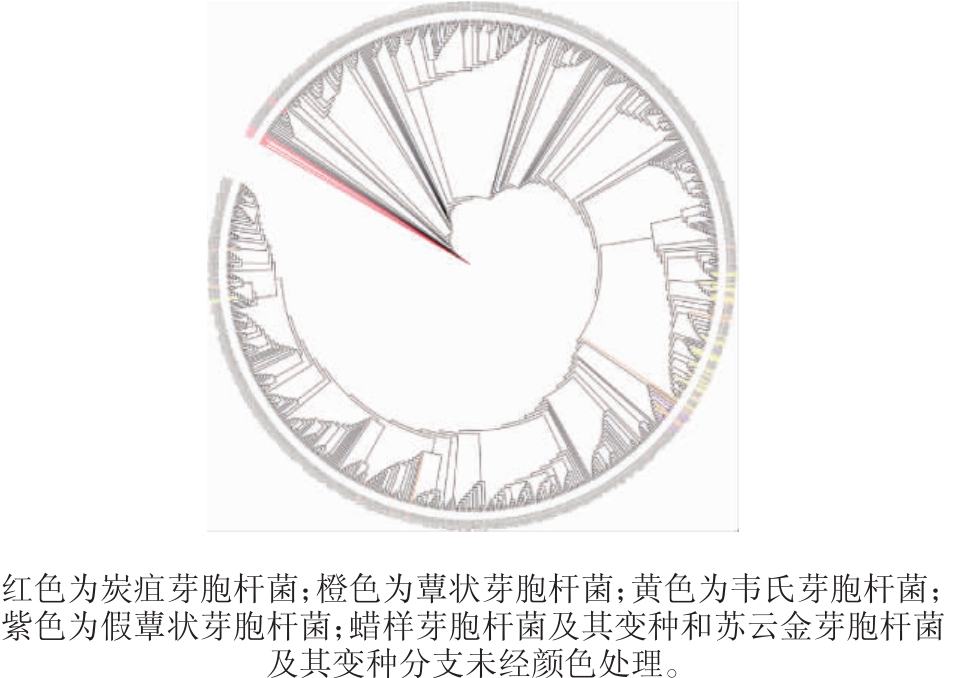
图3 蜡样芽胞杆菌群7对管家基因联合系统进化树
Fig.3 Phylogenetic tree of Bacillus cereus group based on 7 pairs of housekeeping genes
由图3可知,系统进化树的进化情况与MST的情况基本一致。炭疽芽胞杆菌、韦氏芽胞杆菌、蕈状芽胞杆菌、假蕈状芽胞杆菌在进化树中的分布也相对比较集中,其中,炭疽芽胞杆菌在进化树中的分布主要集中在一个进化分支上。韦氏芽胞杆菌和部分蕈状芽胞杆菌集中在同一支上,两者难于区分。
LIU Y等[28]采用多种生物信息学方法分析蜡样芽胞杆菌群遗传情况发现,采用pyc基因对GeneBank数据库中224个蜡样芽胞杆菌菌株的分型效果最好。因此,以Bacillus cereus PubMLST数据库中菌株的pyc基因序列构建系统进化树,结果见图4。由图4可知,pyc基因对蜡样芽胞杆菌群的分型效果与图3非常接近,可见pyc基因序列分型效果确实良好。
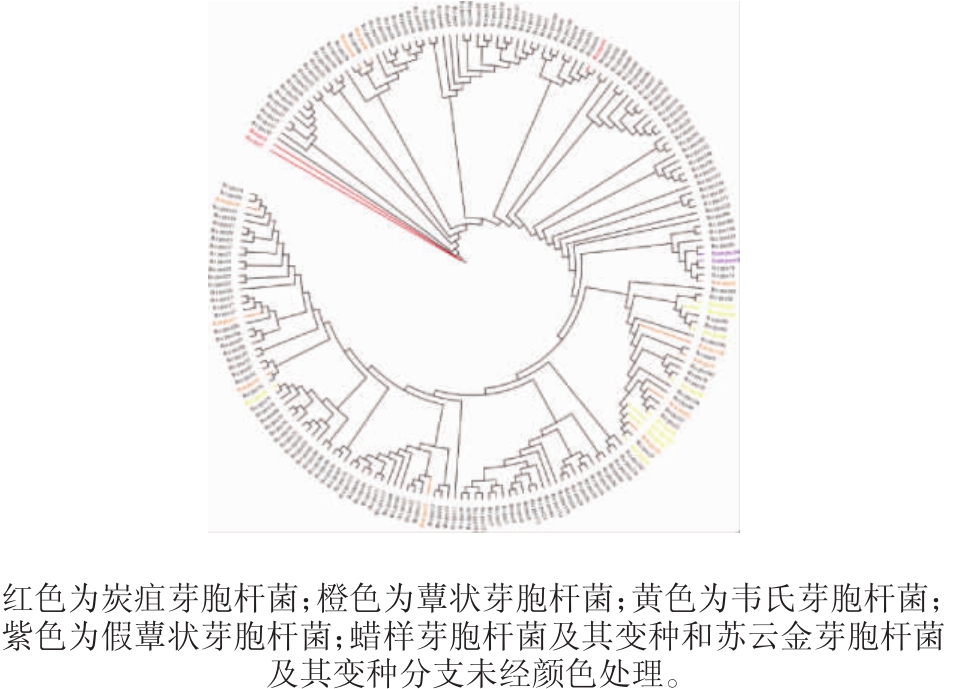
图4 蜡样芽胞杆菌群pyc基因系统进化树
Fig.4 Phylogenetic tree of Bacillus cereus group based on pyc gene
2.2.3 NJ法蜡样芽胞杆菌群的系统进化树分析
采用NJ法构建炭疽芽胞杆菌、部分蜡样芽胞杆菌和苏云金芽胞杆菌及其变种7对管家基因联合的系统进化树,结果见图5。
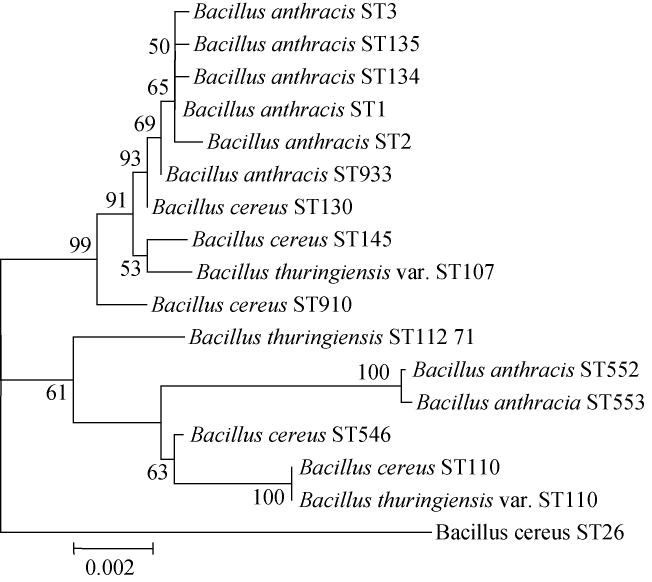
图5 炭疽芽胞杆菌、蜡样芽胞杆菌和苏云金芽胞杆菌及其变种7对管家基因联合系统进化树
Fig.5 Phylogenetic tree of Bacillus anthracis,Bacillus cereus,Bacillus thuringiensis and its varieties based on 7 housekeeping genes
从图5可以看出,在系统进化树中炭疽芽胞杆菌的6个ST集中在同一个进化分支上,但ST552和ST553则在临近并相对独立的一个进化分支上,与部分蜡样芽胞杆菌和苏云金芽胞杆菌混杂在一起。其中ST552和ST553分离株来源于中国,从牛的血液中分离[29],但尚未见到关于这两个菌株的具体病理和毒性分析的深入报道,无法进一步判断这两株炭疽芽胞杆菌的特性,有研究显示,除南极洲以外,所有大陆都有地方性炭疽病疫源地[30]。
炭疽芽胞杆菌、部分蜡样芽胞杆菌和苏云金芽胞杆菌及其变种的管家基因及部分ST见表2。现今提交的炭疽芽胞杆菌的ST共有8个[26]:1、2、3、134、135、552、553、933。其核心型ST1分别与ST3、ST134、ST135和ST933仅有1对管家基因编号有差别,ST1与ST3的glp管家基因编号分别为1和2,两者有1个碱基对差异;ST1与ST134的pta管家基因编号分别为1和57,两者有1个碱基对差异;ST1与ST135的gmk管家基因编号分别为1和39,两者有1个碱基对差异;ST1与ST933的glp管家基因编号分别为1和53,两者有5个碱基对差异。ST1与ST2在ilv和pyc两个管家基因编号存在差异,共有2个碱基差异。ST552和ST553均与核心型ST1有5个管家基因编号不同,且均共有54个碱基差异。而ST552与ST553两者之间仅有1个管家基因编号不同,两者有1个碱基对差异,但是和其他炭疽芽胞杆菌差别较大。炭疽芽胞杆菌甚至和部分Bc、Bt、Bt变种的更为相似,显示出炭疽芽胞杆菌在总体上的高度保守性和部分分化,与图2和图3分析吻合。
表2 炭疽芽胞杆菌、蜡样芽胞杆菌和苏云金芽胞杆菌及变种的管家基因及ST
Table 2 Housekeeping genes and ST of Bacillus anthracis,Bacillus cereus,Bacillus thuringiensis and its varieties
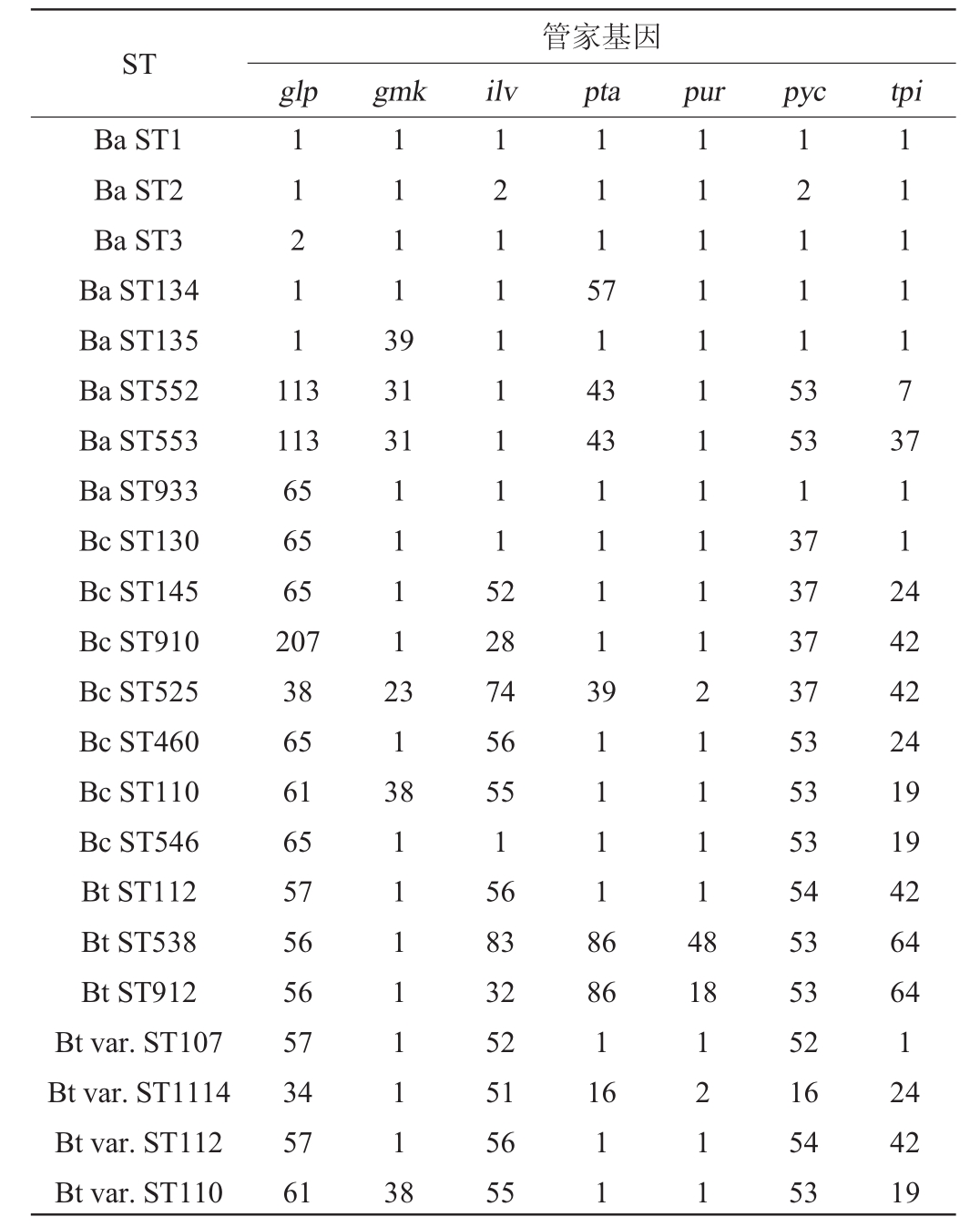
ST Ba ST1 Ba ST2 Ba ST3 Ba ST134 Ba ST135 Ba ST552 Ba ST553 Ba ST933 Bc ST130 Bc ST145 Bc ST910 Bc ST525 Bc ST460 Bc ST110 Bc ST546 Bt ST112 Bt ST538 Bt ST912 Bt var.ST107 Bt var.ST1114 Bt var.ST112 Bt var.ST110管家基因glp gmk ilv pta pur pyc tpi 11211 11113 9 1115 113 113 65 65 65 207 38 65 61 65 57 56 56 57 34 57 61 31 31 714 3 121115 3 1211111115 2 43 1111173 11112 7112 4 313 11113 811111113 8 28 74 56 55 1 56 83 32 52 51 56 55 911118 6 11111111111211114 8 86 1 16 18 11 1211 53 1 37 37 37 37 53 53 53 54 53 53 52 16 54 53 42 42 24 19 19 42 64 64 1 24 42 19
韦氏芽胞杆菌、蕈状芽胞杆菌与假蕈状芽胞杆菌7对管家基因联合的系统进化树见图6。由图6可知,蕈状芽胞杆菌ST445、ST696、ST970和假蕈状芽胞杆菌集中在一个分支上,另两个进化分支均为蕈状芽胞杆菌和韦氏芽胞杆菌的混合分布,两者的进化关系较接近,说明用7对管家基因联合建系统发育树的方式是很难将两者分开的,韦氏芽胞杆菌与蕈状芽胞杆菌在菌落形态上差异很大,两者部分菌株却有一定的亲缘性。
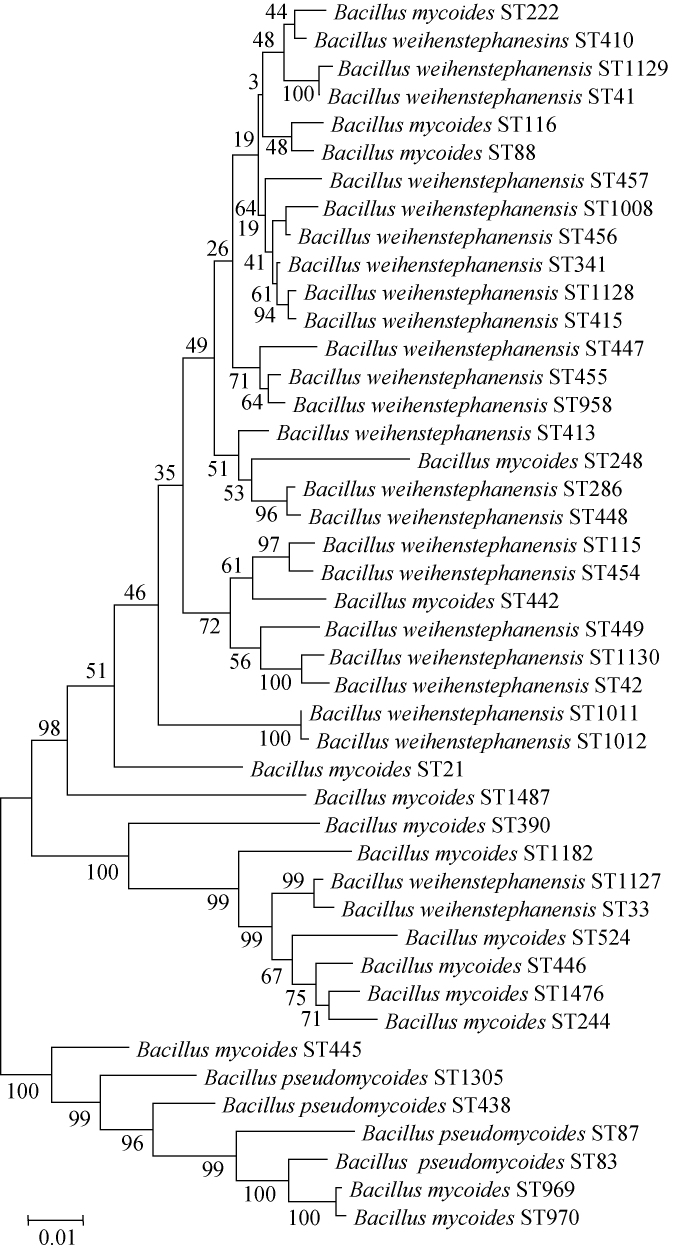
图6 韦氏芽胞杆菌、蕈状芽胞杆菌及假蕈状芽胞杆菌7对管家基因联合系统进化树
Fig.6 Phylogenetic tree of Bacillus weihenstephanensis,Bacillus mycoides and Bacillus pseudomycoides based on 7 pairs of housekeeping genes
3 结论
该研究从Bacillus cereus PubMLST数据库中筛选得到1 329株完整的蜡样芽胞杆菌菌株信息,其中蜡样芽胞杆菌(Bacillus cereus)及变种864株、苏云金芽胞杆菌(Bacillus thuringiensis)及变种345株、炭疽芽胞杆菌(Bacillusanthracis)61株、韦氏芽胞杆菌(Bacillus weihenstephanensis)、蕈状芽胞杆菌(Bacillus mycoides)、假蕈状芽胞杆菌(Bacillus pseudomycoides)分别为33、21和5株。通过Phyloviz Mega和IQ-tree软件研究蜡样芽胞杆菌菌群的种群结构和进化关系发现,蜡样芽胞杆菌菌群内占比很高的蜡样芽胞杆菌和苏云金芽胞杆菌具有丰富而复杂的遗传多样性,相互交织地散布于群内几乎所有的进化分支上,两者无法区分;炭疽芽胞杆菌在进化树上位于相对独立而保守的一个分支;韦氏芽胞杆菌与蕈状芽胞杆菌虽然在菌落形态上差异很大,但两者在系统进化树上位于同一个分支,同源性极高。
[1]CEUPPENS S,BOON N,UYTTENDAELE M.Diversity of Bacillus cereus group strains is reflected in their broad range of pathogenicity and diverse ecological lifestyles[J].Fems Microbiol Ecol,2013,84(3):433-450.
[2]WANG C,SUI Z,LECLERCQ S O,et al.Functional characterization and phylogenetic analysis of acquired and intrinsic macrolide phosphotransferases in the Bacillus cereus group[J].Environ Microbiol,2015,17(5):1560-1573.
[3]郭刚,马琪奇,李炫,等.蜡状芽胞杆菌群三大类全基因组序列的同源性分析[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2010,29(5):994-998.
[4]GUINEBRETIÈRE M H,AUGER S,GALLERON N,et al.Bacillus cytotoxicus sp.nov.,is a novel thermotolerant species of the Bacillus cereus group occasionally associated with food poisoning[J].Int J Syst Evol Micr,2013,63(Pt 1):31-40.
[5]JIMÉNEZ G,URDIAIN M,CIFUENTES A,et al.Description of Bacillus toyonensis sp.nov.,a novel species of the Bacillus cereus group,and pairwise genome comparisons of the species of the group by means of ANI calculations[J].Syst Appl Microbiol,2013,36(6):383.
[6]MILLER R A,BENO S M,KENT D J,et al.Bacillus wiedmannii sp.nov.,apsychrotolerantand cytotoxic Bacilluscereus group speciesisolated from dairy foods and dairy environments[J].Int J Syst Evol Micr,2016,66(11):4744-4753.
[7]LIU B,LIU G H,HU G P,et al.Bacillus bingmayongensis sp.nov.,isolated from the pit soil of Emperor Qin"s Terra-cotta warriors in China[J].Anton Leeuw,2014,105(5):501-510.
[8]JUNG M Y,PAEK W K,PARK I S,et al.Bacillus gaemokensis sp.nov.,isolated from foreshore tidal flat sediment from the Yellow Sea[J].J Microbiol,2010,48(6):867-871.
[9]JUNG M Y,KIM J S,PAEK W K,et al.Bacillus manliponensis,sp.nov.,a new member of the Bacillus cereus group isolated from foreshore tidal flat sediment[J].J Microbiol,2011,49(6):1027-1032.
[10]HU X,HANSEN B M,EILENBERG J,et al.Conjugative transfer,stability and expression of a plasmid encoding a cry1Ac gene in Bacillus cereus group strains[J].Fems Microbiol Lett,2004,231(1):45-52.
[11]YUANY M,HUX M,LIUHZ,et al.Kinetics of plasmid transfer among Bacillus cereus group strains within lepidopteran larvae[J].Arch Microbiol,2007,187(6):425-431.
[12]PATINO-NAVARRETE R,SANCHIS V.Evolutionary processes and environmental factors underlying the genetic diversity and lifestyles of Bacillus cereus group bacteria[J].Res Microbiol,2017,168(4):309-318.
[13]曹飞扬,王娉,江连洲,等.蜡样芽胞杆菌分型方法研究进展[J].食品科学,2017,38(17):286-290.
[14]HALL B G.Building phylogenetic trees from molecular data with MEGA[J].Mol Biol Evol,2013,30(5):1229-1235.
[15]RIBEIRO-GONÇALVES B,FRANCISCO A P,VAZ C,et al.PHYLOViZ Online:web-based tool for visualization,phylogenetic inference,analysis and sharing of minimum spanning trees[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2016,44(W1):W246-W251.
[16]ZHOU X,SHEN X X,HITTINGER C T,et al.Evaluating fast maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic programs using empirical phylogenomic data sets[J].Mol Biol Evol,2018,35(2):486-503.
[17]KALYAANAMOORTHY S,MINH B Q,WONG T K F,et al.Model-Finder:fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates[J].Nat Methods,2017,14(6):587-589.
[18]JOLLEY K A,BRAY J E,MAIDEN M C J.Open-access bacterial population genomics:BIGSdb software,the PubMLST.org website and their applications[J].Wellcome Open Res,2018,3:124.
[19]NASCIMENTO M,SOUSA A,RAMIREZ M,et al.PHYLOViZ 2.0:Providing scalable data integration and visualization for multiple phylogenetic inference methods[J].Bioinformatics,2017,33(1):128-129.
[20]FRANCISCO A P,VAZ C,MONTEIRO P T,et al.PHYLOViZ:phylogenetic inference and data visualization for sequence based typing methods[J].Bmc Bioinformatics,2012,13(1):87.
[21]姬小薇,廖亚玲,毛旭虎,等.MLST分析在病原微生物基因分型应用中的研究进展[J].国际检验医学杂志,2011,32(2):246-249.
[22]FRANCISCO A P,BUGALHO M,RAMIREZ M,et al.Global optimal eBURST analysis of multilocus typing data using a graphic matroid approach[J].Bmc Bioinformatics,2009,10(1):152.
[23]KATOH K,TOH H.Recent developments in the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program[J].Brief Bioinformatics,2008,9(4):286-298.
[24]KATOH K,KUMA K,TOH H,et al.MAFFT version 5:improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2005,33(2):511-518.
[25]LAM-TUNG N,SCHMIDT H A,ARNDT V H,et al.IQ-TREE:a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies[J].Mol Biol Evol,2015,32(1):268-274.
[26]JOLLEY K A,MAIDEN M C.BIGSdb:Scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level[J].Bmc Bioinformatics,2010,11(1):595.
[27]NAKAMURA L K.Bacillus pseudomycoides sp.nov.[J].Int J Syst Bacteriol,1998,48(3):1031-1035.
[28]LIU Y,LAI Q,GÖKER M,et al.Genomic insights into the taxonomic status of the Bacillus cereus group[J].Sci Rep,2015,5:14082.
[29]左庭婷,李岩伟,韩雪莲,等.两株炭疽芽胞杆菌MLST新序列型(ST)[J].微生物学报,2012,52(1):120-123.
[30]VAN ERT M N,EASTERDAY W R,HUYNH L Y,et al.Global genetic population structure of Bacillus anthracis[J].Plos One,2007,2(5):e461.